Company Profile
CnergyFund helps owners and developers of renewable energy mini-grid projects to solicit funds for their projects. In partnership with other bodies, CnergyFund oversees the project’s design and development and manages the negotiation process of trading carbon credits developed through quality standards like Gold Standard Verified Emission Reduction (GS VERs) or Verra’s Verified Carbon Units (VCUs) generated by the client’s project.
Sub-Saharan Africa accounts for a disturbing 75% of the 759 million people in the world living without access to electricity. Nigeria, DR Congo, and Ethiopia top the chart with 118 million persons (15.5%) of the world’s population who are without electricity. As a result, many farmers and business owners spend exorbitant rates on powering generators, causing them to spend more and save less.
CnergyFund was born out of the need to combat the electricity issues in African communities by providing access to clean and affordable energy (SGD 7) to tackle poverty (SDG 1), zero hunger (SDG 2), good health and well-being (SDG 3), quality education (SDG 4), gender equality (SDG 5), decent work and economic growth (SDG 8), and climate action (SDG 13).
CnergyFund provides an accessible platform for renewable energy mini-grid projects through debt financing from impact investors and the voluntary carbon offset market.
What are Carbon Emissions?
Carbon dioxide (CO2), also identified as a greenhouse gas is a colourless, odourless, and harmless gas formed through respiration in living organisms when carbon combusts. Other greenhouse gases besides CO2 include methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorocarbons. These gases are known collectively as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e).
Emission refers to the process by which greenhouse gases and their prototypes are released into the atmosphere over a given range and period of time.
Therefore, Carbon Emissions are Carbon dioxide (CO2) emitted from burning fossil fuels in vehicles, industrial processes, buildings, and cement manufacturing.
Sources of Carbon Emissions
Carbon emissions come from natural and human sources.
Natural Sources
- Volcanic eruptions – Only 0.3% of the natural emissions caused by volcanic eruptions are Carbon dioxide. Other components from the eruption include magma, dust, ash, and gases. The most popular gases erupted by volcanoes are water vapor, sulfur dioxide, and carbon dioxide.
- Soil respiration and decomposition – Soil respiration and decomposition are a natural source of carbon dioxide, making up about 28.56% of natural emissions. Many soil organisms produce energy through respiration. Some of them are decomposers responsible for breaking down dead organic material. In the process of respiration and decomposition, carbon dioxide is emitted as a byproduct.
- Plant and animal respiration – Another natural source of carbon dioxide, covering 28.56% of natural emissions is plant and animal respiration. The chemical reaction plants and animals use to produce energy gives off carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
- Ocean-atmosphere exchange – Ocean-atmosphere exchange covers the highest source of natural carbon dioxide emissions (42.84%). The dissolved carbon dioxide in oceans is emitted into the atmosphere at the top of the sea.
Human Sources
- Land use change/Deforestation – Land use change occurs when the natural environment is transformed for agricultural purposes and human settlement. Deforestation is the complete cutting down of forest trees. Its effect on greenhouse gas emissions makes it the most crucial type of land use change to watch. The removal and clearance of forest trees cause the release of a great number of greenhouse gases, thereby increasing the carbon dioxide level. Globally, land use change consumes 3.3% of human carbon dioxide emissions.
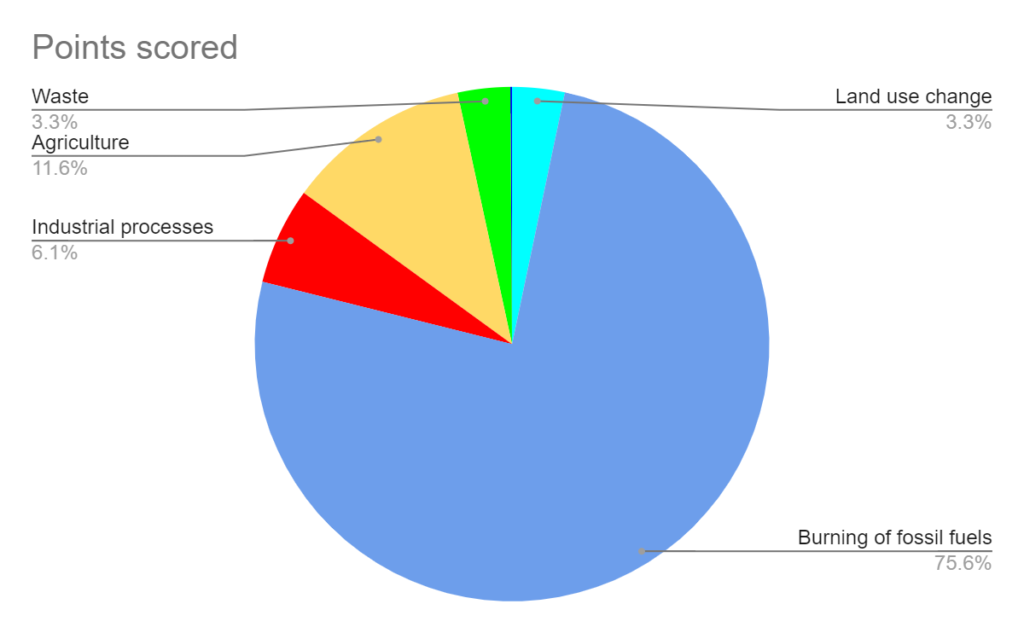
Source: Climate Watch, based on raw data from IEA (2021), GHG Emissions from Fuel Combustion, www.iea.org/statistics; modified by WRI.
![]()
- Burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas – Combustion of fossil fuels produce the highest source of human carbon dioxide emissions, standing at 75.6%. The heat, electricity, or power used for transportation is generated from the energy emitted after burning fossil fuels.
Most common types of fossil fuels
- Coal, takes 40% of global carbon dioxide emissions, reaching an all-time high of 15.3 billion tonnes in 2021
- Oil, responsible for 10.7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions in 2021
- Natural gas, amounts to 7.5 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions in 2021
Three major economic sectors operate on fossil fuels. They are:
- Electricity/Heat (produced 31.8% of carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel combustion in 2019)
- Transportation (produced 17% of carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel combustion in 2019)
- Industry (produced 12.7% of carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel combustion in 2019)
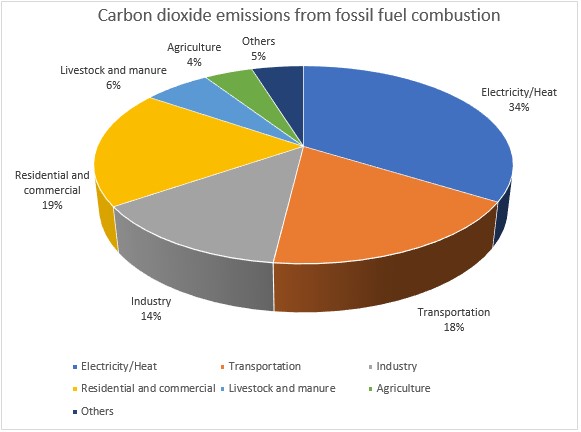
Source: World Greenhouse Gas Emissions in 2019
In 2020, the Electricity/Heat and Transportation sectors produced around 52% of global carbon dioxide emissions.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Practices – Industrial practices are responsible for 6.1% of human carbon dioxide emissions. The emitted carbon dioxide comes as a byproduct of the chemical reactions involved in the industrial production process.
The industrial processes that majorly produce carbon dioxide emissions are:
- The production of iron and steel.
- The production of cement.
- The production of chemicals
- The production of petrochemicals.
Carbon Credits
Carbon credits are permits that enable the company or project proprietor to emit a given amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) or other greenhouse gases. One carbon credit allows one ton of carbon dioxide (CO2), or its direct proportion in other greenhouse gases, to be emitted.
Companies are given credits that limit the amount of pollution that can be released over a given period. If the company does not use up the credits eventually, it can sell them to another company that needs them. Companies with emission reduction projects are thereby compensated for reducing CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions.
CnergyFund and its partners oversee the development of the carbon project to qualify developers’ projects for the carbon credits.
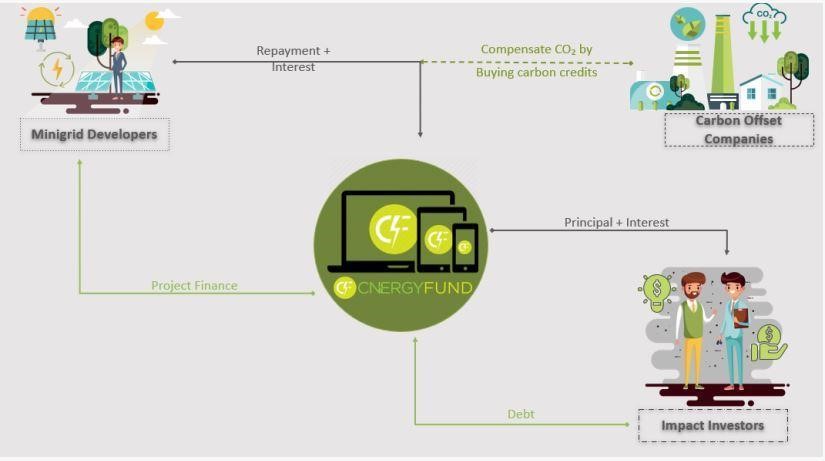
How it works
Renewable energy mini-grid projects are developed using standards such as Gold Standard Verified Emission Reduction (GS VERs) or Verra’s Verified Carbon Units (VCUs) which the project owners can trade with companies who offset their unavoidable carbon emissions on impact projects. The income generated from the sale of their credits can help to settle some of the interests on the loan facility.
For further enquiries about CnergyFund’s impact projects, you can send an email to info@cnergyfund.com.
References
https://cnergyfund.com/
https://cnergyfund.com/2022/04/01/crowdfunding-for-clean-energy-towards-zero-hunger-and-no-poverty/
https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-co2-emissions-in-2021-2
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/carbon_credit.asp
https://www.lawinsider.com/dictionary/carbon-emissions#:~:text=Carbon%20Emissions%20means%20carbon%20dioxide,Protocol%2C%20which%20warm%20the%20atmosphere.
https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Glossary:Carbon_dioxide_emissions
https://whatsyourimpact.org/greenhouse-gases/carbon-dioxide-emissions
Content produced courtesy of Stephanie Pius Akpan and Adebayo Ajowele.

